restraint_type selects the types of the generated restraints. Only one restraint type can be selected at a time, except for the stereochemical restraints (BOND, ANGLE, DIHEDRAL, IMPROPER) that can all be calculated at the same time. It is useful to distinguish between the stereochemical restraints and homology-derived restraints. The stereochemical restraints are obtained from libraries that depend on atom and/or residue types only (e.g., CHARMM 22 force field [MacKerell et al., 1998] or statistical potentials), and do not require the alignment aln with template structures. In contrast, the homology-derived restraints are calculated from related protein structures, which correspond to all but the last sequence in the alignment aln (the target). These templates are read from coordinate files, which are the only data files required. All restraints are added to the existing restraints, even if they duplicate them (but see the comment for the 'OMEGA' restraints below).
Stereochemical restraints:
- 'BOND'. This calculates covalent bond restraints (harmonic terms).
It relies on the
list of the atom-atom bonds for MODEL, prepared previously by the
model.generate_topology() command. The mean values and force constants are
obtained from the parameter library in memory. Only those bonds
are restrained that have all or at least restraint_sel_atoms
in the selected atom set 1.
- 'ANGLE'. This calculates covalent angle restraints (harmonic
terms). It relies on the
list of the atom-atom-atom bonds for MODEL, prepared previously by the
model.generate_topology() command. The mean values and force constants are
obtained from the parameter library in memory. Only those angles
are restrained that have all or at least restraint_sel_atoms
in the selected atom set 1.
- 'DIHEDRAL'. This calculates covalent dihedral angle restraints
(cosine terms). It relies on the list of the atom-atom-atom-atom
dihedral angles for MODEL, prepared previously by the model.generate_topology()
command. The minima, phases, and force constants are obtained from the
parameter library in memory. Only those dihedral angles are restrained
that have all or at least restraint_sel_atoms in the selected atom
set 1.
- 'IMPROPER'. This calculates improper dihedral angle restraints
(harmonic terms). It relies on the list of the improper dihedral angles
for MODEL, prepared previously by the
model.generate_topology() command. The mean values and force constants are
obtained from the parameter library in memory. Only those impropers
are restrained that have all or at least restraint_sel_atoms
in the selected atom set 1.
- 'STEREO'. This implies all 'BOND', 'ANGLE', 'DIHEDRAL', and
'IMPROPER' restraints.
- 'SPHERE14'. This constructs soft-sphere overlap restraints (lower
harmonic bounds) for atom pairs separated by exactly three bonds (1-4
pairs). It relies on atom radii from the '$RADII14_LIB' library.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion.
- 'LJ14'. This constructs 1-4 Lennard-Jones restraints using the
modified 1-4 Lennard-Jones parameters from the CHARMM parameter library.
There is no way to calculate 'LJ14' as dynamic restraints.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion.
- 'COULOMB14'. This constructs 1-4 Coulomb restraints by relying
on the atomic charges from the CHARMM topology library.
There is no way to calculate 'COULOMB14' as dynamic restraints.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion.
- 'SPHERE'. This constructs soft-sphere overlap restraints
(lower harmonic bounds) for all atom pairs that are not in bonds,
angles, dihedral angles, improper dihedral angles, nor are explicitly
excluded by the 'E' entries read from a restraint file or added
by the model.restraints.add() command.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion. Note that this makes these restraints
static (i.e., not dynamic) and that you must set energy_data.dynamic_sphere
to False before evaluating the molecular pdf if you want to avoid
duplicated restraints. These restraints should usually not be combined
with the Lennard-Jones ('LJ') restraints.
When intersegment is True, the inter-segment non-bonded restraints are also constructed; otherwise, the segments do not feel each other via the non-bonded restraints. This option does not apply to the model.optimize() command where information about segments is not used at all (i.e., model.optimize() behaves as if intersegment = True).
- 'LJ'. This constructs Lennard-Jones restraints for all atom pairs
that are not in bonds, angles, dihedral angles, improper dihedral angles,
nor are explicitly excluded by the 'E' entries read from a restraint file
or added by the model.restraints.add() command.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion.
Note that this command makes the non-bonded
restraints static (i.e., not dynamic) and that you must set
energy_data.dynamic_lennard
to False before evaluating the molecular pdf if you want to avoid
duplicated restraints. Note that CHARMM uses both 'LJ14' and 'LJ'.
For large molecules, it is better to calculate 'LJ' as dynamic restraints
because you can use distance cutoff energy_data.contact_shell in
model.optimize() to
reduce significantly the number of non-bonded atom pairs.
- 'COULOMB'. This constructs Coulomb restraints for all atom pairs that
are not in bonds, angles, dihedral angles, improper dihedral angles, nor are
explicitly excluded by the 'E' entries read from a restraint file or added
by the model.restraints.add() command.
Only those non-bonded pairs are restrained that have all or at least
energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected atom set 1.
They must also satisfy the residue_span_range & residue_span_sign
criterion.
Note that this command makes the non-bonded restraints
static (i.e., not dynamic) and that you must set
energy_data.dynamic_coulomb
to False before evaluating the molecular pdf if you want to avoid
duplicated restraints. Note that CHARMM uses both 'COULOMB14' and
'COULOMB'. For large molecules, it is better to calculate 'COULOMB'
as dynamic restraints because you can use distance cutoff
energy_data.contact_shell
in model.optimize() to reduce significantly the number of non-bonded atom pairs.
- 'ALPHA'. This makes restraints enforcing an
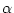 -helix (mainchain
conformation class ``A'') for the residue segment specified by the two
residue_ids (Section 4.9.1). The helix is restrained
by
-helix (mainchain
conformation class ``A'') for the residue segment specified by the two
residue_ids (Section 4.9.1). The helix is restrained
by 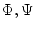 binormal restraints, N-O hydrogen bonds,
binormal restraints, N-O hydrogen bonds,
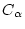 -
-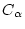 distances for
distances for
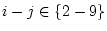 ,
, 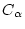 -O distances
for
-O distances
for
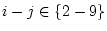 ,
and O-O distances for
,
and O-O distances for
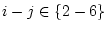 . These target distances were all
obtained from a regular
. These target distances were all
obtained from a regular 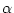 -helix in one of the high-resolution myoglobin
structures. A convenient way to add 'ALPHA', 'STRAND', or 'SHEET'
restraints to the calculation by the 'model' script is to include them
in the special_restraints routine (Section 1.8,
Question 12). Note that at least the non-hydrogen mainchain
atoms topology model is required although the same functionality could also
be provided for the
-helix in one of the high-resolution myoglobin
structures. A convenient way to add 'ALPHA', 'STRAND', or 'SHEET'
restraints to the calculation by the 'model' script is to include them
in the special_restraints routine (Section 1.8,
Question 12). Note that at least the non-hydrogen mainchain
atoms topology model is required although the same functionality could also
be provided for the 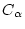 -only topology with small changes to the source
code.
-only topology with small changes to the source
code.
- 'STRAND'. This makes restraints enforcing an extended strand
conformation for the residue segment specified by the two residue_ids
(Section 4.9.1). This is achieved by applying
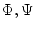 binormal restraints only. These binormal restraints force the mainchain
conformation into class ``B'', except for the Pro residues which are
restrained to class ``P'' [Šali & Blundell, 1993].
binormal restraints only. These binormal restraints force the mainchain
conformation into class ``B'', except for the Pro residues which are
restrained to class ``P'' [Šali & Blundell, 1993].
- 'SHEET'. This calculates H-bonding restraints for a pair of
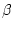 -strands. atom_ids specifies the two atom identifiers
(Section 4.7.1) defining the first H-bond in the
-strands. atom_ids specifies the two atom identifiers
(Section 4.7.1) defining the first H-bond in the 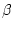 -sheet
ladder. sheet_h_bonds specifies the number of H-bonds to be added.
The parallel and anti-parallel sheets are selected by a positive and negative
integer in sheet_h_bonds, respectively. In a parallel sheet, hydrogen
bonds start at the first or the second term of the following series
(depending on atom_ids): 1N:1O, 1O:3N, 3N:3O, 3O:5N, etc. For an
anti-parallel sheet, the corresponding series is 1N:3O, 1O:3N, 3N:1O,
3O:1N, etc; note that the residue indices are always decreasing for the
second strand. The extended structure of the individual strands must be
enforced separately by the 'STRAND' restraints if so desired.
-sheet
ladder. sheet_h_bonds specifies the number of H-bonds to be added.
The parallel and anti-parallel sheets are selected by a positive and negative
integer in sheet_h_bonds, respectively. In a parallel sheet, hydrogen
bonds start at the first or the second term of the following series
(depending on atom_ids): 1N:1O, 1O:3N, 3N:3O, 3O:5N, etc. For an
anti-parallel sheet, the corresponding series is 1N:3O, 1O:3N, 3N:1O,
3O:1N, etc; note that the residue indices are always decreasing for the
second strand. The extended structure of the individual strands must be
enforced separately by the 'STRAND' restraints if so desired.
- 'USER_DISTANCE'. This makes distance restraints between pairs
of atoms from set 2 and 3 (inter-set only), using the value of
restraint_parameters. Only distances satisfying the
residue_span_range criterion are restrained. This command
is useful for making non-specific ``compactization'' restraints.
Homology-derived restraints:
For these restraints, the input alignment aln must be given.
- 'DISTANCE'. This makes distance restraints
that are generated for all pairs of atoms
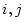 where
atom
where
atom 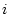 is from selected set 2 and atom
is from selected set 2 and atom 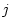 is from selected set 3
(as defined by the model.pick_atoms() command). The atoms also have to be
within the residue spanning range specified by
residue_span_range = r1 r2, such that the residue index
difference
is from selected set 3
(as defined by the model.pick_atoms() command). The atoms also have to be
within the residue spanning range specified by
residue_span_range = r1 r2, such that the residue index
difference
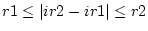 when residue_span_sign =
False and
when residue_span_sign =
False and
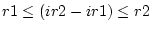 when residue_span_sign =
True. Moreover, for a restraint to be created, at least one distance in the
template structures must be less than maximal_distance (in ).
The mean of this basis pdf is equal to the template distance and its standard
deviation
when residue_span_sign =
True. Moreover, for a restraint to be created, at least one distance in the
template structures must be less than maximal_distance (in ).
The mean of this basis pdf is equal to the template distance and its standard
deviation 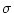 is calculated from an analytic model specified by
distance_rsr_model. Use model 5 for
is calculated from an analytic model specified by
distance_rsr_model. Use model 5 for  -
-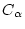 distances and model
6 for N-O distances. For models 1 through 6, this standard deviation is
transformed by
distances and model
6 for N-O distances. For models 1 through 6, this standard deviation is
transformed by
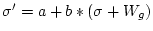 where
where 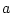 and
and 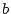 are given
by restraint_stdev and
are given
by restraint_stdev and 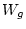 is a gap weighting function of the form
is a gap weighting function of the form
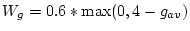 .
. 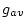 is the average distance of the
two residues involved in the restraint from a gap. For models 3 through 6,
this is additionally transformed by
is the average distance of the
two residues involved in the restraint from a gap. For models 3 through 6,
this is additionally transformed by
![$\sigma'' = \sigma' + \sum_{i}[d+e*\max(0,f-g_{i})]$](img116.png) where the sum is over each
of the atoms
where the sum is over each
of the atoms 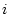 involved in the distance,
involved in the distance, 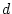
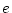 and
and 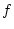 are given by
restraint_stdev2, and
are given by
restraint_stdev2, and 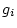 is the distance of each residue from a gap.
The first six models are polynomials and depend on several structural features
of the template and its similarity to the target. The polynomial
coefficients are specified in library file '$PARAMS_LIB'. When
``polynomial model'' 7 is selected, the standard deviation of restraints
is set to constant
is the distance of each residue from a gap.
The first six models are polynomials and depend on several structural features
of the template and its similarity to the target. The polynomial
coefficients are specified in library file '$PARAMS_LIB'. When
``polynomial model'' 7 is selected, the standard deviation of restraints
is set to constant 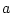 . Each basis pdf in the distance pdf corresponds
to one template structure with an equivalent distance.
The weights of basis pdf's depend on local sequence similarity between
the target and the templates when basis_pdf_weight = 'LOCAL'
and on global sequence identity when basis_pdf_weight = 'GLOBAL'.
In addition, the atom pairs restrained by homology-derived restraints
must by default not be in a chemical bond, chemical angle, dihedral angle,
or on an excluded pairs list. This behavior can be changed by resetting
energy_data.excl_local (see model.optimize()).
. Each basis pdf in the distance pdf corresponds
to one template structure with an equivalent distance.
The weights of basis pdf's depend on local sequence similarity between
the target and the templates when basis_pdf_weight = 'LOCAL'
and on global sequence identity when basis_pdf_weight = 'GLOBAL'.
In addition, the atom pairs restrained by homology-derived restraints
must by default not be in a chemical bond, chemical angle, dihedral angle,
or on an excluded pairs list. This behavior can be changed by resetting
energy_data.excl_local (see model.optimize()).
- 'CHI1_DIHEDRAL', 'CHI2_DIHEDRAL',
'CHI3_DIHEDRAL', 'CHI4_DIHEDRAL', 'PHI_DIHEDRAL', 'PSI_DIHEDRAL',
'OMEGA_DIHEDRAL', 'PHI-PSI_BINORMAL' are the mainchain and sidechain
dihedral angle restraints. Only those dihedral angles are restrained that
have all or at least energy_data.nonbonded_sel_atoms in the selected
atom set 1. The means and standard deviations for the dihedral
Gaussian restraints are obtained from the $RESDIH_LIB and
$MNCH?_LIB libraries and their weights from the MDT tables,
which are read in as specified by MDT_LIB in $LIB/libs.lib.
The large MDT tables give the conditional weights for each possible dihedral
angle class, as a function of all possible combinations of features on which
a particular class depends. If dih_lib_only is ON or there is
no equivalent residue in any of the
templates, the weights for the dihedral angle classes depend only on
the residue type and are obtained from the '$RESDIH_LIB' and
'$MNCH?_LIB' libraries; the dih_lib_only argument allows
one to force the calculation of the ``homology-derived'' mainchain
and sidechain dihedral angle restraints that ignore template information.
basis_pdf_weight has the same effect as
for the distance pdf's.
When MODELLER's 'OMEGA' restraints are calculated, the currently existing
restraints on atoms 'O C +N +CA' in all residues are automatically deleted.
These deleted restraints correspond to the improper dihedral angles
involving the
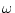 atoms. They are deleted because they could be
``frustrated'' by the new 'OMEGA' restraints. No action is taken with
regard to any of the previously existing, possibly duplicated dihedral angle
restraints. Thus, to avoid restraint duplication, including that of the
'OMEGA' restraints, call the model.restraints.condense() command after all
the restraints are calculated.
atoms. They are deleted because they could be
``frustrated'' by the new 'OMEGA' restraints. No action is taken with
regard to any of the previously existing, possibly duplicated dihedral angle
restraints. Thus, to avoid restraint duplication, including that of the
'OMEGA' restraints, call the model.restraints.condense() command after all
the restraints are calculated.
basis_relative_weight is the cutoff for removing weak basis pdf's from poly-Gaussian feature pdf's: a basis pdf whose weight is less than the basis_relative_weight fraction of the largest weight is deleted.