change selects an optimization (when equal to 'OPTIMIZE') or randomization (when equal to 'RANDOMIZE'):
- When optimizing, this command finds the first selected restraint
that restrains the specified dihedral angle of each selected residue.
It then sets the value of that dihedral to the most likely value.
A residue is selected if any of its atoms is in the set 1 of selected
atoms.
- When randomizing, the command changes the specified dihedral angle
of each selected residue by adding a random value distributed uniformly
from
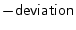 to
to
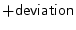 degrees.
degrees.
dihedrals can be either a vector of dihedral angle names or a
single string containing all the dihedral angle names separated by
blanks. The dihedral angles involved in cyclic structures are not changed
(e.g., sidechain dihedral angles in disulfide bonds and prolines).
The dihedral angles that can be changed are listed at the top
of the $RESDIH_LIB library: alpha, phi, psi, omega,
chi1, chi2, chi3, chi4, chi5. Dihedral angle 'alpha' is the
virtual ![]() dihedral angle defined by four consecutive
dihedral angle defined by four consecutive
![]() atoms.
atoms.
The bond connectivity of the MODEL has to exist before this command is executed. If you read in the model by model.read(), the bond connectivity is defined by subsequent calls to topology.append() and model.generate_topology() (also make sure that sequence entry does not exist in the alignment or that no alignment is in memory).